Segnation paging
segmation_paging分段分页
动机
- Solution to fragmentation(碎片): permit(允许) the logical address space of processes to be noncontiguous(不连续).
- The view of memory is different between
- logical (programmer’s ): a variable-sized(可变大小的) segments
- physical : a linear(线性的) array of bytes
- The hardware could provide a memory mechanism(机制) that mapped(映射) the logical view to the actual(实际的) physical memory.
分段
划分段
将:
1 | void f(){ //在未划分段时,地址时连续的,从 0 开始直至结束 |
划分为:
1 | 0.void f(){ //划分段后每段的起始地址为 0 ,每个段有对应的标号,段与段之间不需要连续 |
在分段之后的程序中,访问逻辑地址需要表明段号和偏移
注意:上述代码前的标号代表指令而非C语言语句
由于内存被分成了许多段,而且段与段之间并不连续,这就意味着需要一张段表来存放对应的信息用来寻找对应的逻辑地址
段表:段号,基址,限长
当拿到一个逻辑地址<段号:偏移>时,首先将段表内相应段号对应的基址值存放到base寄存器中,将对应的段限长存放到limit寄存器中,先执行保护(比较偏移与段限长,若未超过段限长则说明地址有效)后进行转换(物理地址 = base + offset)
逻辑地址 16位段式地址转换实例
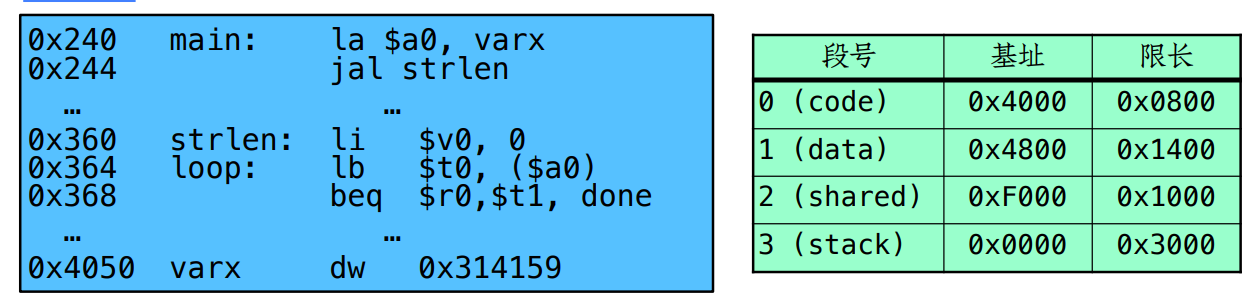
假设逻辑地址的段号占2bits,段内位移占14bits,此时 PC寄存器的值为0x240
下⼀条指令的物理地址为:
PC:0b0000 00,10 0100 0000
故段号为0
下一条指令物理地址:0x4000 + 0x240 = 0x4240
Move 0x4050 → $a0, Move PC+4 → PC,下条指令物理地址为:
PC由0x240 变为 0x244:0000 0010 0100 0100
短号为 0
吓一跳物理地址为 0x4000 + 0x244 = 0x4244
Move 0x0248 → $ra (return address!), Move 0x0360 → PC,下条指令物理地址为:
上述汇编指令意味着,将 0x0248存放到ra寄存器中(做函数的返回地址)
将PC寄存器中的值更新为 0x0360:0000 0011 0110 0000
对应短号为 0下一条物理地址为:0x4000 + 0x0360 = 0x4360
Move 0x0→$v0, Move PC+4→PC,下条指令物理地址为:0x4364
“lb $t0,($a0)”(将a0寄存器中所示内存地址处取出1个字节存到寄存器t0中),该内存地址为:
a0中存放的值为:0x4040:0b0100 0000 0101 0000
对应的段为 1
运行时物理内存为:0x4800 + 0x50 = 0x4850
分段并没有完全解决外部碎片的问题
分页
基本方案
将内存看作是由若干个相等大小的分区组成,我们称这个分区为帧或页框
将进程也分为与帧大小相同的若干个,称为页面,只有切割进程的最后一块可能小于页面大小

如图:将内存分为 19 块等大的帧,进程分为 11 块等大的页面,将这 11个等大的页面离散的存放在memory中,当然就需要一张表用于存放帧的使用情况,记录了页面也页框的对应情况这个表被称为页表
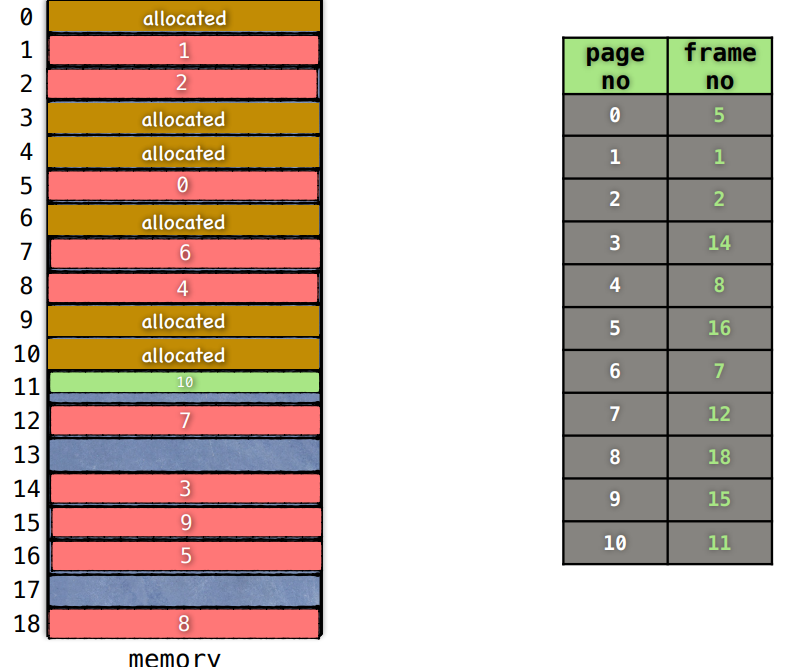
分页后指令的逻辑地址将从 0 开始,为了确定物理地址,就必须确定页面号与页内偏移,根据页面号通过查询页表找到对应的页框号,从而确定物理地址
physical address = frame_no * pagesize + offset
操作系统在进行分页地址转换时,直接将页面号替换为页框号与页内偏移进行拼接即可获得物理地址
分页硬件
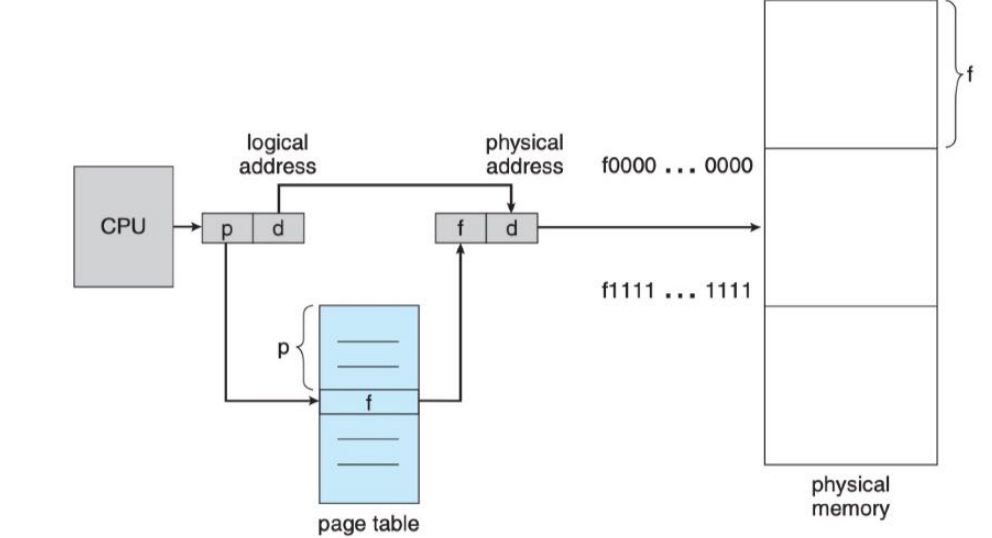
CPU根据逻辑地址<页面号,页偏移>,根据页面号查询页表找到对应的段号,将段号与段偏移拼接,得到物理地址
LOGICAL ADDRESS
- The page size (like the frame size) is defined by the hardware. The size of a page is a power of 2(2的幂次), varying(更改) between 512 bytes and 1 GB per page, depending(依赖) on the computer architecture(架构). (大小为2的幂次是为了可以拼接运算,目前大多数计算机采用页面大小为 4k)
- The selection of a power of 2 as a page size makes the translation(转化) of a logical address into a page number and page offset particularly(特别的) easy.
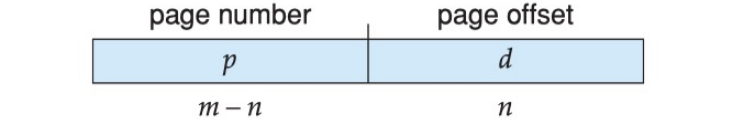
- If the size of the logical address space is 2m , and a page size is 2n bytes, then the high-order
m − nbits of a logical address designate(指定为) the page number, and thenlow-order bits designate the page offset. Thus, the logical address is as follows:
分页与分段的区别